Integrating Employee Well-being into Your ESG Strategy
What if your next competitive advantage wasn't a new product but a healthier, more supported workforce? As businesses increasingly focus on ESG, many employers are beginning to ask the right questions.
How do we support our people better? How do we make well-being part of how we operate, not just a set of side benefits? Employee well-being is no longer a peripheral benefit confined to HR policies; it has become a vital component of an organization's overall health. It has become a business priority.
When your people are mentally resilient, financially secure, physically healthy, and part of an inclusive culture, your company becomes stronger across the board. You see higher engagement, better retention, lower absenteeism, and a workplace culture people want to be part of.
Moreover, it directly contributes to improving your ESG performance. So, how do you make it happen? That's precisely what this guide is here to answer. We'll walk you through the four key pillars of wellness. Those pillars are mental health, financial wellness, workplace culture, and physical health. Each one ties back to measurable ESG outcomes.
We'll also show you how to build into your ESG wellness roadmap with clear, actionable steps. You'll learn how to assess employee needs, implement targeted programs, use wellness tech effectively, and report your progress with frameworks like GRI and SASB.
Would you like tangible proof of its effectiveness? We've included examples from companies across industries that are doing this well. You'll see what they're doing, why it's working, and how you can apply similar strategies in your workplace.
If you're serious about ESG, it's time to take wellness seriously, too - not just because it's suitable for your team but also because it's beneficial for your business. Ready to start? Let's dig in.
Why Well-Being Matters in ESG Frameworks

Employee well-being has come a long way. It's no longer a reactive measure rolled out when burnout hits or engagement dips. Today, it's a proactive strategy that sits at the heart of responsible business. Companies are no longer asking whether wellness belongs in the ESG conversation. They're figuring out how to embed it into every layer of their operations.
And there's a good reason for that. Investing in well-being directly supports ESG objectives. It boosts employee engagement, improves retention, and builds a workplace culture where people feel seen, supported, and empowered.
Wellness is now a performance driver and a true reflection of a company's commitment to social responsibility. When employees are mentally strong, financially confident, physically healthy, and part of a positive culture, they contribute more, stay longer, and speak highly of their workplace. That's the kind of energy that powers sustainable growth and a stronger ESG profile.
To make this actionable, we break wellness down into four core pillars: mental health, financial wellness, workplace culture, and physical health. These aren't just buzzwords. They're building blocks for a resilient workforce and a company that's ready for the future. Let's explore each one of them.
The Four Pillars of Employee Well-Being in ESG
Employee wellness is not a one-off program or an isolated HR initiative. It is a comprehensive framework built around four key pillars: mental health, financial wellness, workplace culture, and physical health.
These pillars do more than improve employee morale. They shape how people experience their work and directly influence an organization's performance on ESG metrics.
As ESG becomes a benchmark for how companies operate, treat people, and manage risk, well-being has taken center stage. It forms a tangible part of the "Social" component and influences how responsibly an organization governs its workforce. Let's explore how each wellness pillar contributes to ESG success.
1. Mental Health

Supporting mental health is no longer optional. High-stress levels, burnout, and emotional fatigue are workplace realities, and they come with a cost.
Companies that offer mental health days, access to counseling, peer support networks, and manager training see measurable improvements in employee engagement and emotional resilience.
This directly supports the social pillar of ESG. A company that prioritizes psychological well-being creates safer, more inclusive spaces for people to work. It also reduces absenteeism, turnover, and reputational risk.
From a governance angle, leaders who actively invest in mental health demonstrate that the organization can manage human capital responsibly and with empathy.
Check out our guide: Your All-in-One Corporate Mental Wellness Guide For Employers
2. Financial Wellness
When employees feel in control of their finances, they are more focused and confident at work. Programs that support financial literacy, savings goals, retirement planning, and debt management not only reduce stress but also lead to better job performance and stronger retention.
Financial wellness goals are closely tied to the social component of ESG. It promotes fairness, economic security, and workforce stability. It also reinforces Governance goals by reflecting ethical pay practices, transparency in benefits, and long-term planning for employee success.
Companies that track financial wellness outcomes and include them in their ESG reports demonstrate a serious commitment to building economic resilience across their teams.
3. Workplace Culture

Culture is the invisible structure that holds a company together. It shapes everything from day-to-day interactions to long-term business outcomes.
A positive workplace culture, where employees feel included, heard, and recognized, leads to higher engagement, innovation, and trust. This pillar strongly supports the social side of ESG. Companies that invest in equity, diversity, inclusion, and employee voice build a more just and balanced workplace.
Culture also ties into governance by promoting ethical behavior, clear communication, and accountability. A well-governed culture does not just boost internal morale. It enhances the organization's perception among investors, customers, and communities.
4. Physical Health
Physical health is the foundation of daily productivity. When companies invest in safe workspaces, ergonomic setups, fitness challenges, and preventative care, they reduce sick days and improve overall well-being.
This ties directly to the social element of ESG by ensuring that employees work in safe and supportive conditions. In industries where physical labor is involved, this also connects to compliance with safety regulations and health reporting.
Physical wellness can support environmental goals when companies combine health efforts with sustainability, like promoting green commuting or serving eco-friendly meals.
From a Governance perspective, tracking physical health metrics such as participation rates, reduced injuries, or improved health screening results builds trust and shows accountability.

Together, these four pillars create a strong foundation for any company serious about its ESG performance. They transform broad values like sustainability and responsibility into daily actions that employees can take to heart.
By supporting the mental, financial, cultural, and physical health of your workforce, you're not just improving internal outcomes; you're meeting ESG goals in a way that's real, measurable, and built to last.
Implementing Well-Being Strategies to Strengthen ESG Goals
A well-being strategy should not rely on assumptions or short-term enthusiasm. It requires structure, intention, and a clear link to your organization's ESG vision.
When thoughtfully designed, wellness strategies support employee satisfaction, reduce organizational risk, and demonstrate a long-term commitment to people-first values. Below is a detailed breakdown of each implementation step, complete with purpose, importance, and practical execution.
1. Surveys Employees and Assess their Wellness Needs
Purpose:
-
Employee wellness surveys identify what your employees need when it comes to their well-being.
-
Pinpoint wellness gaps across departments, demographics, or locations.
Importance:
-
Without input, wellness initiatives risk being out of touch or underutilized.
-
Listening directly to your people builds trust and shows your commitment to inclusion and transparency; both critical ESG values.
Implementation:
-
Run anonymous surveys, pulse checks, and focus groups quarterly or biannually.
-
Ask about mental health, financial stress, work-life balance, physical health, and workplace satisfaction.
-
Use tools like Google Forms, Qualtrics, or third-party HR platforms to track responses and trends over time.

2. Wellness Programs: Mental Health and Financial Wellness
Purpose:
- Provide structured support for everyday stressors impacting employee performance.
Importance:
-
Mental and financial health are top concerns for employees globally.
-
Addressing them proactively reduces burnout, improves focus, and demonstrates social responsibility.
-
These programs also help companies meet expectations under the Social pillar of ESG.
Implementation:
-
Offer access to mental health professionals, EAPs, therapy reimbursements, and stress-relief resources.
-
Offer workshops or one-on-one sessions on financial planning, debt reduction, and retirement savings.
-
Regularly update program offerings based on usage data and employee feedback.
3. Create an Inclusive Culture: Support Well-Being for All

Purpose:
- Build an environment where every employee feels seen, respected, and supported; regardless of background.
Importance:
-
Inclusion fuels engagement, productivity, and psychological safety.
-
It is a cornerstone of ESG's Social pillar and increasingly a metric tracked by investors and rating agencies.
Implementation:
-
Roll out DEI training, support Employee Resource Groups, and review HR policies for bias.
-
Celebrate cultural awareness days, establish mentorship programs, and ensure leadership reflects the diversity of the workforce.
-
Evaluate inclusivity through employee engagement surveys and qualitative feedback.
4. Wellness Technology: Track and Enhance Well-Being
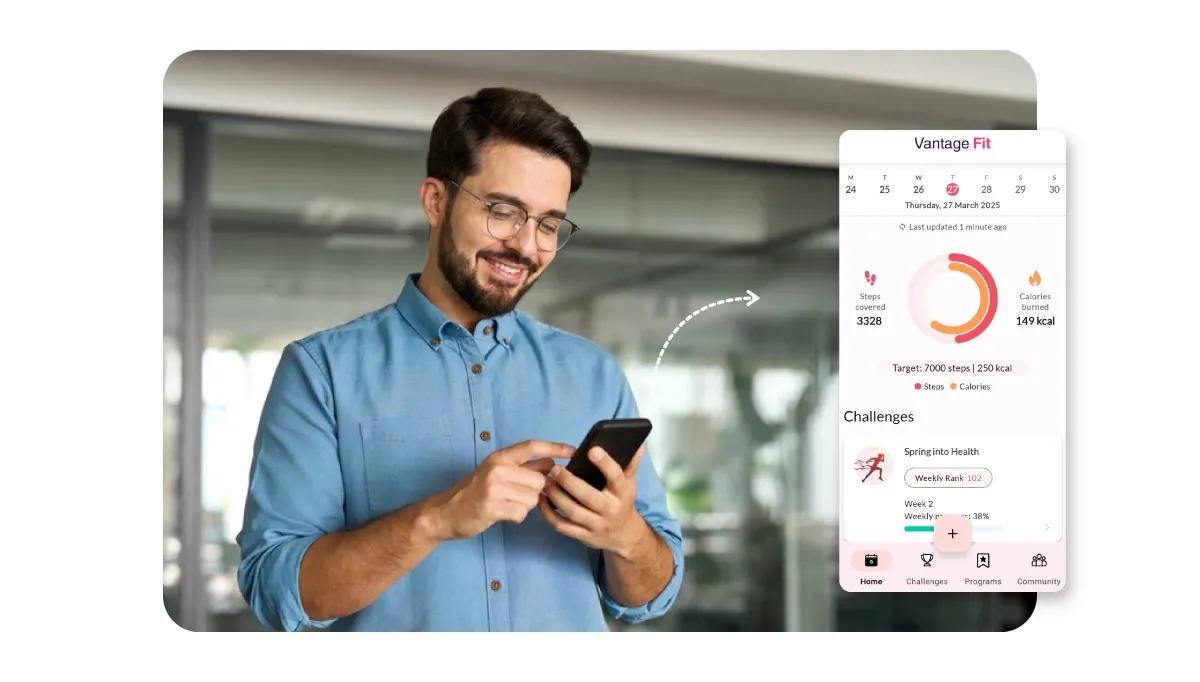
Purpose:
- Enhance wellness by making it more engaging, scalable, and measurable through digital tools.
Importance:
-
Technology enables real-time tracking, personalized experiences, and data-driven decision-making.
-
It supports ESG's Governance pillar by improving transparency and accountability.
Implementation:
-
Introduce wellness apps or portals offering self-assessments, habit tracking, virtual challenges, and content libraries.
-
Utilize dashboards to track participation and wellness trends throughout the organization.
-
Partner with vendors that prioritize data privacy and user confidentiality.
5. Metrics for Well-Being Success: Measure impact
Purpose:
- Evaluate whether your wellness strategy is delivering results.
Importance:
-
What gets measured gets improved.
-
Reporting wellness outcomes aligns with ESG frameworks, such as GRI and SASB, and helps demonstrate ROI.
Implementation:
-
Track absenteeism, turnover, health claims, and employee engagement scores.
-
Include metrics such as program participation, stress reduction reports, and feedback on wellness effectiveness.
-
Publish results in ESG or sustainability reports and use findings to refine strategy.
6. Training and Education: Promote Wellness Awareness
Purpose:
- Equip employees and managers with the knowledge to prioritize and normalize well-being.
Importance:
-
Awareness drives participation.
-
It reduces stigma and increases the usage of wellness resources, supporting ESG's social and governance goals.
Implementation:
-
Conduct workshops on mental resilience, mindfulness, and financial planning.
-
Train managers on emotional intelligence, burnout signals, and having supportive conversations.
-
Incorporate wellness modules into onboarding and leadership development programs.
7. Leadership Support: Ensure Executive Buy-In

Purpose:
- Align wellness with company values and secure long-term commitment from leadership.
Importance:
-
Executive involvement reinforces that wellness is a strategic priority, not a side project.
-
Leadership modeling has a direct influence on employee engagement and culture.
Implementation:
-
Set wellness goals within executive KPIs or ESG dashboards.
-
Encourage leaders to participate in wellness events, share their personal wellness stories, and sponsor well-being campaigns.
-
Allocate budget and internal resources dedicated to well-being initiatives.
8. Social Support: Build a Sense of Community
Purpose:
- Make wellness feel like a shared journey, not an individual task.
Importance:
-
Peer-driven wellness encourages participation, strengthens social bonds, and creates emotional safety.
-
It reinforces ESG values by nurturing a workplace where community and empathy thrive.
Implementation:
-
Create wellness ambassador programs or peer support circles.
-
Host monthly wellness events, team-based fitness challenges, or gratitude rituals.
-
Recognize and reward employees who champion well-being in their teams.
9. Flexible Work Arrangements: Promote Work-Life Balance
Purpose:
- Allow employees to manage their work in a way that fits their personal lives.
Importance:
-
Flexibility is one of the most sought-after wellness benefits and has a significant impact on retention and productivity.
-
It aligns with ESG's Social principles by prioritizing humane and adaptive working conditions.
Implementation:
-
Offer hybrid work models, compressed workweeks, or adjustable start and end times.
-
Implement policies that support caregiving, mental health breaks, or sabbatical planning.
-
Train managers to support flexible schedules while maintaining accountability and performance standards.
Together, these nine strategies provide a structured, scalable, and people-centric approach to wellness. When implemented with care and consistency, they don't just improve lives at work; they help companies lead with purpose, meet ESG standards, and build sustainable success from the inside out.
Now that we've explored how wellness ties into ESG, let's look at how you can measure and report these initiatives to maximize impact and transparency.
Measuring and Reporting Wellness Initiatives in ESG Frameworks
Employee well-being has become a critical component of how companies deliver on their environmental, social, and governance (ESG) strategy. However, to demonstrate genuine commitment, organizations must move beyond intention and begin measuring outcomes.
Metrics bring clarity, help track progress and make it possible to report wellness as a core part of ESG performance. Here's how you can define, align, and report wellness initiatives in a way that adds substance to your environmental, social, and governance ESG efforts.
1. Define Key Wellness Metrics
Purpose:
Establish measurable indicators to evaluate the effectiveness of your wellness initiatives.
Importance:
Without data, it isn't easy to prove impact or demonstrate progress. Defining wellness metrics ensures that your efforts are both targeted and reportable within your Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) framework.
Implementation:
-
Measure employee engagement through regular surveys and pulse checks.
-
Track mental health indicators, including counseling usage, stress-level feedback, and burnout risk.
-
Monitor absenteeism, sick leave, and unplanned time off.
-
Capture productivity improvements using performance trends and team-level outputs.
-
Record participation rates in wellness initiatives such as mental health sessions, fitness programs, or financial planning workshops.
-
Evaluate changes in healthcare costs and claims to assess the long-term financial impact of your wellness investments.
2. Align Metrics with ESG Standards

Purpose:
Ensure wellness performance is integrated into recognized ESG reporting systems.
Importance:
Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) reporting must follow clear standards to remain credible and consistent. Aligning wellness metrics with these standards demonstrates your organization's commitment to accountability and transparency.
Implementation:
-
Use Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) standards, especially GRI 403, to disclose workplace health and well-being efforts.
-
Incorporate SASB (Sustainability Accounting Standards Board) disclosures related to human capital, engagement, and turnover.
-
Position wellness outcomes clearly under the Social pillar of your ESG strategy, showing your commitment to employee care and equity.
-
Tie data and program ownership to leadership oversight to fulfill the Governance pillar, demonstrating responsible management and ethical practices.
3. Reporting Wellness Outcomes
Purpose:
Share the results of your wellness strategy across internal and external channels.
Importance:
Transparent reporting reinforces the value of wellness and adds depth to your Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) narrative. It builds trust with employees, investors, and other stakeholders.
Implementation:
-
Present quantitative results such as reduced absenteeism, increased program engagement, or improved well-being scores.
-
Share cost reductions related to insurance premiums, reduced turnover, or fewer health-related disruptions.
-
Publish outcomes in ESG disclosures, sustainability reports, and annual impact reviews.
-
Add employee testimonials or case studies to highlight the experience lived behind the data, creating a more relatable narrative.
Measuring and reporting wellness is not just a tactical move. It is a strategic approach to connecting people-focused efforts to broader business objectives.
By embedding wellness metrics into your environmental, social, and governance (ESG) framework, you demonstrate that employee health and organizational health are closely intertwined. This not only strengthens your ESG performance but also enhances your culture, reputation, and long-term business resilience.
Final thoughts
Employee wellbeing is now a business priority and a strategic component of any robust environmental, social, and governance (ESG) framework. Investing in mental health, financial security, inclusive culture, and physical health directly contributes to higher engagement, lower turnover, and better long-term performance.
Companies that lead in ESG are those that treat employee wellness as a measurable, reportable, and consistent practice. This is not just about benefits or perks. It is about creating a workplace that is sustainable, equitable, and built for the future.
If you're looking for a structured, data-driven way to begin, Vantage Fit can support your goals. It helps you launch wellness programs, track employee engagement, and generate real-time wellness data that feeds directly into your ESG reporting.
Start integrating wellness into your ESG strategy today. Reach out to learn how Vantage Fit can help make your well-being efforts innovative, scalable, and fully aligned with your ESG goals.
FAQs
1) Is wellness part of ESG?
Yes. Wellness supports the social pillar of ESG by improving employee health, safety, and satisfaction.
2) Does ESG include mental health?
Yes. Mental health is increasingly seen as a critical factor in workplace safety and social sustainability.
3) What is the meaning of ESG?
ESG stands for Environmental, Social, and Governance. It's a framework for sustainable, ethical business practices that prioritize long-term value over short-term profits.
4) What metrics should companies track to measure the impact of wellness programs in ESG?
Track engagement, absenteeism, program participation, healthcare costs, and retention rates.
5) What wellness metrics can be reported in ESG frameworks beyond participation?
Include reductions in sick leave, cost savings, improved satisfaction scores, and lower burnout risk.
6) Can ESG wellness metrics be tracked in real time, and what tools are most effective for this?
Yes. Platforms like Vantage Fit allow you to track participation, engagement, and wellness trends in real-time with built-in analytics.








