Why AI is the Missing Link in Workplace Mental Health (And Why 2026 Is the Tipping Point)
Stress, anxiety, and burnout have skyrocketed since the pandemic. US employers now grapple with absenteeism, turnover, and spiraling healthcare costs—all while productivity losses from mental health issues drain $1 trillion globally each year, as per W.H.O. Traditional employee wellness programs, once the gold standard, now struggle to meet surging demand.
Putting stats into facts, 58% of employees have considered quitting due to mental health struggles!
This unfortunate gap gave rise to an unlikely ally: artificial intelligence. And guess what?
Many employees now express comfort with AI-driven mental health tools, while HR leaders report unprecedented interest in these solutions. The Economist says,
The emergence of generative AI, like ChatGPT, has brought about a substantial surge in public interest in AI, shedding light on how this new technology has the potential to reshape our everyday existence and our cognitive and professional processes.
And they do have a valid point. The most effective AI tools function as early warning systems, analyzing communication patterns to detect burnout risks weeks before symptoms appear.
Yet questions linger. Can algorithms truly understand human emotion? How do we protect privacy while leveraging data? Let's explore how forward-thinking organizations are answering these questions and why 2026 marks the tipping point for AI in corporate wellness.
What's Happening with Employee Mental Health Right Now?
Truth be told, employee mental health has reached a breaking point!
- According to the American Psychological Association, workplace burnout has doubled since the pandemic, jumping from 38% to 76% of employees.
- Gallup's latest workplace research reveals only 23% of employees feel engaged, while 44% experience daily stress.
- Mental health-related sick days have tripled compared to 2019.
Recognizing the urgency, the Vantage Fit team conducted a cross-sector employee survey to gain a deeper understanding of the challenges faced by workers. The results, visualized in the chart below, highlight a troubling spectrum of everyday mental health struggles in today’s workplaces.
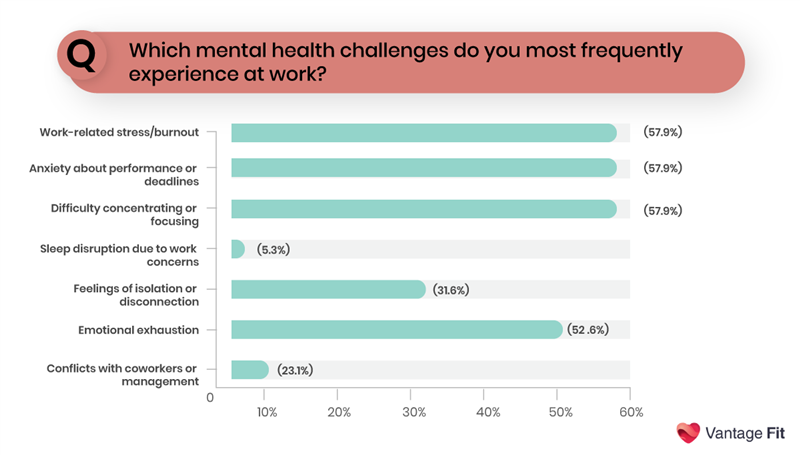
These mental health challenges translate directly into financial hemorrhaging for businesses.
- Absenteeism alone costs employers $3,600 per hourly worker annually, with mental health as the primary driver.
- In some sectors, companies face high turnover rates, where replacing each employee costs 50-200% of their annual salary.
- Healthcare premiums continue climbing as mental health claims now consume 30% of Employee Assistance Program resources—up from just 3% ten years ago.
Traditional support systems are struggling to cope under this pressure.
Employee Wellness Programs reach only 3-5% of eligible workers, while therapy wait times stretch from 6 to 8 weeks in major cities. Corporate wellness initiatives often provide superficial solutions—such as meditation apps and one-off workshops—that fail to address systemic issues. Worse, many employees avoid company-sponsored mental health resources due to stigma concerns.
AI-powered platforms, on the other hand, offer 24/7 accessibility, personalized interventions, and anonymous support that scales across entire organizations.
A Deloitte global research shows that 75% of respondents expect to change their talent strategies within two years in response to GenAI. The Digital mental health market is set to grow from $23.63 billion in 2024 to $27.56 billion in 2025, with corporate wellness as the fastest-growing segment.
Major employers, such as Microsoft, Google, and Johnson & Johnson, have integrated AI-based mental health tools, reporting measurable improvements in both employee satisfaction and productivity.
Such advancements, right?
Let's explore how AI is transforming mental health support in the workplace.
How is AI Transforming the Way We Support Mental Health at Work?
AI is generally defined as a subdiscipline of computer science that aims to produce programs that simulate human intelligence.
– American Psychological Association
It is dramatically reshaping the landscape of mental health support in the workplace, transitioning from basic clinical referrals to sophisticated, proactive systems. This evolution is rooted in the history of AI's application in mental healthcare, which traces back to the mid-20th century with early efforts to simulate cognitive processes.
Pioneers like Allen Newell and Herbert A. Simon conducted foundational research on AI models of human problem-solving. A notable early technological step was the development of ELIZA in the late 1960s and early 1970s. It was an interactive chatbot designed to simulate a psychotherapist, which offered a glimpse into the potential of technology for mental health interactions.
Tap here to have some chit-chat with ELIZA. Users often found ELIZA surprisingly engaging, sometimes forming emotional connections and feeling as though they were conversing with a real person. The "ELIZA effect" describes this phenomenon, where people attribute human-like understanding and empathy to a simple computer program that lacks genuine comprehension.
Over time, AI's role expanded with the emergence of expert systems in the 1980s, which aimed to provide diagnostic and treatment recommendations and the development of computerized cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) programs in the late 20th century.
This journey, marked by a series of evolutionary milestones, reflects a growing recognition of technology's potential to support and enhance mental well-being, moving beyond reactive approaches to integrated, data-informed support.
AI's transformative impact on workplace mental health support can be observed across several major categories of tools:
1. Detection and Monitoring Systems
These tools use AI to assess mental health by analyzing diverse data sources to identify early signs of stress, burnout, or emotional distress. AI can monitor and analyze real-time data related to employees' mental health, including their mood, stress levels, and work fatigue, to provide feedback and recommendations for personal care.
Few of the techniques used are:
-
Sentiment Analysis - It utilizes Natural Language Processing (NLP) to analyze text from sources such as social media posts, chat logs, or diaries for emotional tone and sentiment.
-
Voice Analysis - It can detect alterations in speech patterns, including variations in pitch, tone, and rhythm, which may indicate conditions such as anxiety or depression.
-
Facial Expression Analysis - Often combined with computer vision, it provides insights into emotional states by detecting micro-expressions and subtle changes in facial features, which is beneficial for remote monitoring through video consultations or mobile apps.
Wearable devices, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers equipped with AI, can continuously monitor physiological and behavioral markers, including heart rate variability, sleep patterns, physical activity, and speech patterns.
AI algorithms analyze this data to identify deviations from baseline, offering early insights into changes in mental health. AI can also analyze electronic health records (EHRs) and other patient data to identify patterns suggesting a mental health condition, flagging at-risk patients for healthcare providers.
Continuous monitoring, powered by AI, enables the early detection of relapses or deteriorations, alerting individuals and providers to timely intervention.
2. AI-powered Chatbots and Virtual Assistants
These digital entities can engage in empathetic conversations, provide coping strategies, and deliver therapeutic interventions such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) techniques.
Examples include Woebot and Wysa, which utilize AI and evidence-based therapeutic approaches users with human help when needed. These tools are particularly valuable in addressing the shortage of mental health professionals and providing scalable, cost-effective alternatives to traditional therapy by interacting with multiple users simultaneously.
They offer anonymous support options, which can help reduce the stigma associated with seeking mental health help by creating a safe environment for individuals to access resources without disclosing their identities. The sophistication of conversational AI allows these chatbots to engage in empathetic and therapeutic dialogues, providing emotional support and delivering interventions.
3. Personalized Recommendation Engines
They leverage AI's capability to analyze vast datasets to create customized wellness programs and suggest tailored interventions. By analyzing an individual employee's unique characteristics, needs, behavioral patterns, preferences, and real-time physiological data, AI algorithms can customize treatment plans.
This comprehensive analysis enables AI to tailor interventions, ensuring that appropriate support is matched to each employee. It can include recommending personalized stress-relief exercises, mindfulness programs, virtual therapy sessions, or suggesting modifications to work habits based on detected patterns of stress or burnout.
AI can analyze data from genetic tests, brain imaging, and electronic health records to predict a patient's response to various treatments, including antidepressant medications, and determine optimal personalized treatment plans.
Companies like Google, Accenture, and SAP utilize AI to personalize wellness programs and provide customized resources tailored to individual needs.
4. Data Analytics for Organizational Insights
It involves AI analyzing diverse data sources at an organizational level to provide insights into employee well-being trends and potential risk factors.
AI can analyze data from employee engagement surveys, attendance patterns, productivity levels, communication behaviors, and feedback platforms to spot early warning signs of mental distress or identify psychosocial risk factors.
By detecting shifts in employee sentiment, collaboration patterns, or work habits, AI can help HR departments and managers anticipate mental health challenges and implement proactive support systems or adjust policies.
AI systems can also effectively identify and mitigate risks by monitoring compliance and identifying potential hazards, such as predicting occupational accidents or monitoring compliance with safety legislation.
Balancing AI interventions with human-led support systems is crucial for delivering the best care, where AI handles routine tasks and initial support, while mental health professionals focus on more complex and sensitive aspects.
What Makes AI So Effective for Supporting Employee Mental Health?
Understanding the mechanisms behind AI's effectiveness in workplace mental health reveals a fascinating intersection of technology and human psychology. Let’s find out how AI is topping the charts in looking after employee mental health:
1. 24/7 Accessibility and Immediate Intervention
Mental health doesn’t operate on a 9-to-5 schedule—and neither should your support system.
Yet, traditional support systems often operate within rigid timeframes. AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants transform this limitation by providing immediate, 24/7 support regardless of time or location.
These systems eliminate the need for appointment scheduling, reduce waiting periods, and provide immediate help during critical moments when employees experience acute stress or anxiety.
Beyond mere availability, AI systems provide a consistent quality of interaction regardless of when employees engage. Unlike human counselors who may experience fatigue or varying emotional states, AI maintains the same level of empathy and therapeutic guidance at 3 AM as it does at 3 PM, ensuring reliable support during vulnerable moments.
The World Health Organization reports a significant shortage of mental health professionals, particularly in underserved areas.
2. Scalability and Cost-Effectiveness
AI-driven platforms can support 1,000 employees as effectively as 100,000 concurrently while maintaining personalized, high-quality interactions.
Besides, economic analysis reveals significant cost advantages of AI-powered mental health support.
Unmind’s data shows organizations gain $6,565 annually per employee through reduced presenteeism when combining AI tools with human coaching.
As per research, organizations can implement comprehensive mental health support programs at a fraction of the cost of hiring additional human therapists or expanding traditional Employee Assistance Programs.
3. Reduced Stigma through Anonymous and Private Digital Interactions
AI-powered mental health support effectively addresses one of the most significant barriers to seeking help: stigma. Anonymity creates a safe space for employees to explore their mental health concerns without the anxiety associated with face-to-face interactions.
Our survey revealed that 47.4% of people preferred the autonomy that comes with anonymity.
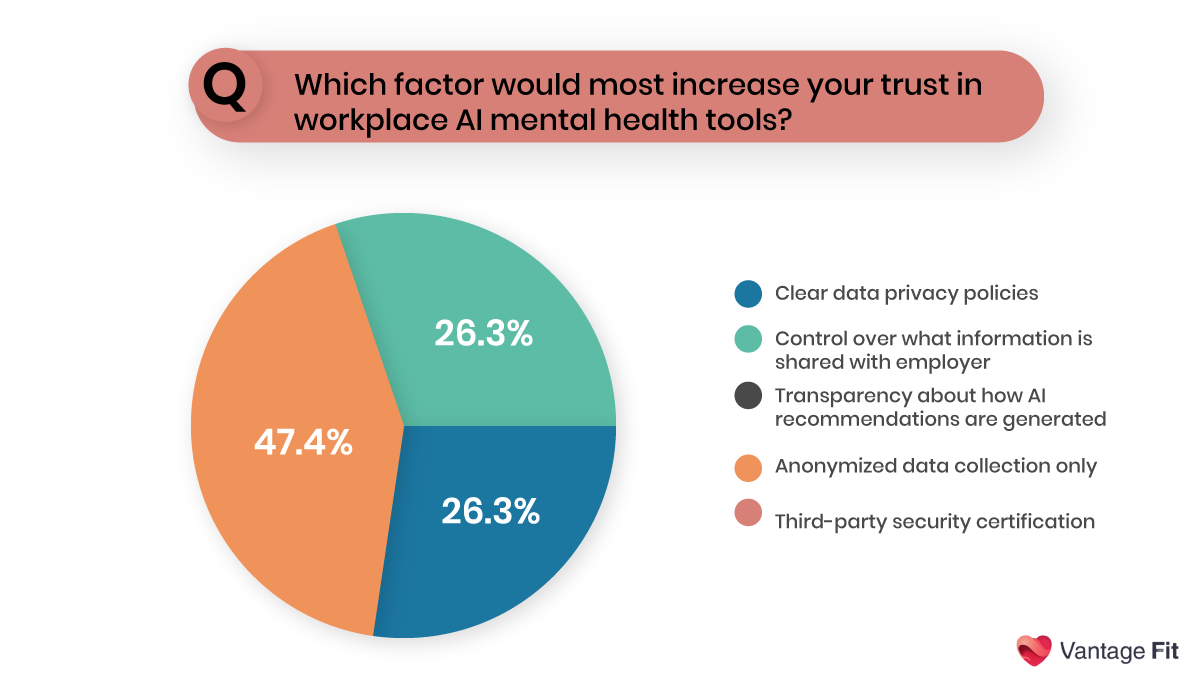
The absence of human judgment enables more honest self-disclosure.
AI systems can provide support without requiring employees to disclose personal information to human colleagues or supervisors, maintaining professional boundaries while still addressing mental health needs. Source
Platforms offering anonymous support, such as Wysa, have successfully helped over 5 million users worldwide, showing the effectiveness of stigma-free mental health resources.
4. Early Detection of Potential Mental Health Issues
Machine learning algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify early signs of mental health issues before they escalate into more serious conditions. A study reveals that AI can detect cognitive overload through subtle indicators, such as delayed email responses, increased error rates, or reduced meeting participation.
Not just that. Predictive capabilities extend beyond individual risk assessment to organizational-level insights. It could be based on various factors, including workload patterns, team dynamics, and even environmental changes.
These early warning systems allow for timely interventions that can prevent the escalation of mental health issues, reducing both human suffering and organizational costs.
5. Personalization of Support
AI excels at creating highly personalized interventions by analyzing vast datasets, including:
- communication patterns,
- behavioral indicators, and
- individual preferences.
Machine learning algorithms can process information from electronic health records, physiological responses, and genetic data to identify the most effective treatment strategies tailored to each employee.
Woebot’s CBT interventions demonstrate 31% higher efficacy when tailored to the user's vocabulary and cultural context.
Moreover, AI continuously learns and adapts its recommendations based on user feedback and engagement patterns.
6. Integration with Existing Health Benefits
Modern AI systems function as force multipliers for EAPs, handling routine interactions while escalating high-risk cases. Three Wire Systems reports that blended human-AI models increase EAP utilization from 8% to 34% by reducing initial access barriers.
Mphasis’ enterprise solution routes 65% of inquiries through AI triage, freeing human advisors to focus on crisis management and complex care coordination. This integration creates a continuum of care where AI handles 24/7 support and progress monitoring while humans provide nuanced therapeutic aids.
7. Good Financial Returns
Longitudinal studies reveal AI mental health tools deliver measurable financial returns through multiple pathways:
- Productivity: 10-15% gains in task completion rates after 4-6 AI coaching sessions.
- Retention: 28% reduction in turnover among frequent platform users.
- Healthcare Costs: $13,200 annual savings per employee in mental health claims.
Unmind’s 4.6x ROI model combines these factors, showing that every $1 invested yields $3.49 in productivity gains and $1.11 in reduced healthcare costs. For global enterprises, this equates to $4.6 million in net returns per 1,000 employees annually.
What Are the Biggest Challenges When Implementing AI Mental Health Solutions?
1. Data Privacy and Security Vulnerabilities
Mental health data is extraordinarily sensitive, and breaches can have devastating consequences. The recent Confidant Health breach exposed 5.3 terabytes of sensitive mental health records, highlighting the critical need for robust encryption and secure storage solutions.
Many AI mental health chatbots aren't even considered medical devices under US law, creating loopholes that allow pharmaceutical companies to access sensitive patient information.
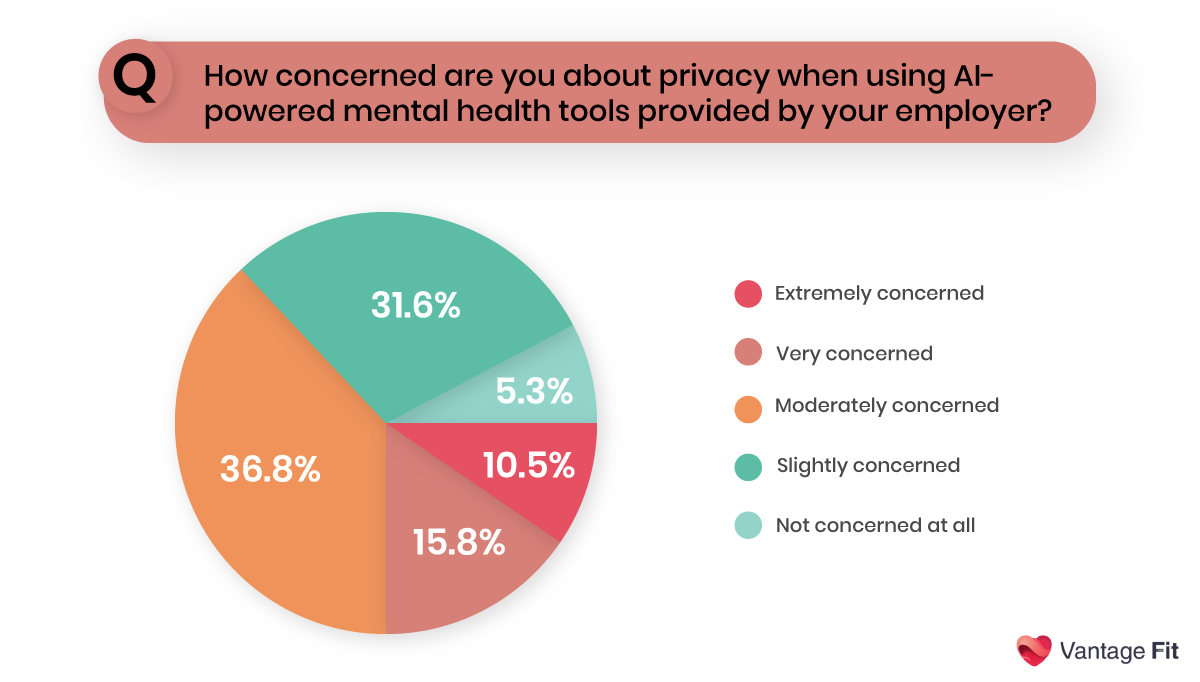
2. Lack of Human Empathy
Despite advances, AI cannot replicate the therapeutic alliance crucial for recovery. Research reveals that 89% of people value the emotional intuition of human therapists over algorithmic responses. Over-reliance on AI risks creating transactional care models—62% of therapists report that AI tools feel "emotionally sterile".
Dharitri Dutta, a certified psychologist who we interviewed for this piece, warns:
I don’t feel it’s a healthy practice to be emotionally dependent on AI. It comes with numerous risks. Humans not only talk through words, but non-verbal communication is also equally important when we try to understand a person. AI may lack in this regard.
Although, yes, AI does come with the ability to analyze micro-expressions but it has a lot of drawbacks as well. Rudolf Eremyan, a pioneer in the field of NLP and Machine Learning, points that it misses out on :
- Irony and sarcasm
- Types of negations
- Word ambiguity
- Multipolarity
3. Algorithmic Myopia
Many AI models are predominantly trained on Western data, making them less effective for diverse populations. A 2024 study revealed that ethnic minorities experience a 23% higher misdiagnosis rate in AI-driven assessments. This algorithmic bias can result in incorrect diagnoses and inappropriate treatments, particularly for underrepresented groups.
4. Cultural Readiness and Implementation Pitfalls
Organizational resistance derails the effectiveness of AI mental health initiatives. Key barriers include:
- Generational divides: Gen Z employees adopt AI tools 3x faster than Baby Boomers.
- Leadership alignment: Only 29% of executives receive training on AI mental health ethics.
5. Accuracy Limitations
Thought models like KTU’s depression detector achieve 97.5% accuracy in controlled settings, real-world performance varies significantly.
Dr. Rytis Maskeliūnas cites,
The main problem with these studies is the lack of data because people tend to remain private about their mental health matters.
Due to a lack of data, the training of AI systems is hindered. It also demonstrates how AIs can become obsolete if not fed and updated with sufficient data regularly.
6. Workplace Behavior Misinterpretation
AI models analyzing productivity metrics frequently pathologize standard work patterns. Microsoft’s Work Trend Index found:
- AI-driven productivity metrics often misinterpret non-linear work patterns common among high performers and creative roles.
- AI's tendency to pathologize neurodivergent work styles without proper training data.
In fact, 34% of neurodivergent employees reported receiving irrelevant AI wellness suggestions in pilot programs.
7. Regulatory and Compliance Issues
Only 3% of 20,000 mental health apps meet clinical validation standards. HIPAA permits limited data sharing during crises, but employees often misunderstand these exceptions—43% mistakenly believe employers can access therapy chatbot logs without consent.
While these challenges are significant, they're not insurmountable. The key lies in developing AI tools with ethics, inclusivity, accuracy, and safety in mind while ensuring robust regulation and human oversight.
And things should be made clear to the users.
Now, let’s read the next section to comprehend how a company can run an AI-based mental health program.
How Do You Successfully Roll Out an AI Mental Health Program?
1. Organizational Readiness Assessment
Before deploying any technology, conduct a 360-degree needs analysis:
- Assess EHR integration capabilities and data security protocols.
- Initiate workshops to address algorithmic bias and privacy concerns.
- Use anonymous surveys to gauge openness to AI tools.
Below is a snapshot of one of the most important questions asked on our survey to gauge employee preferences for AI mental health tools.
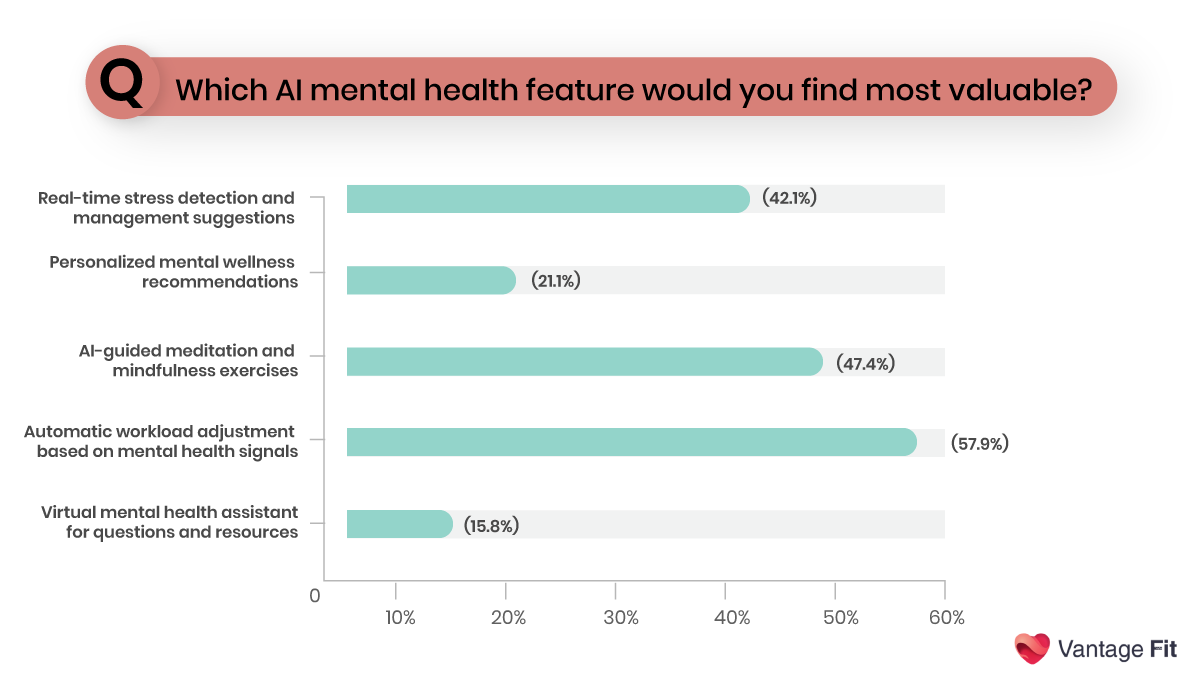
2. AI Tool Selection Criteria
Choose clinically validated, ethically designed platforms. Opt for systems that offer API integration with existing HR platforms to minimize workflow disruptions.
The Framework for AI Tool Assessment in Mental Health (FAITA-Mental Health) is a practical checklist to ensure AI tools used in mental health care—like chatbots or mood-tracking apps—are safe, ethical, and genuinely helpful. It evaluates six key areas:
- scientific reliability (does it use proven methods?),
- user experience (is it easy and respectful to use?),
- crisis handling (can it spot emergencies and connect users to help?),
- user control (can people manage their data and choices?),
- fairness (does it work equally well for diverse groups?), and
- transparency (is it clear how the tool works and who’s behind it?).
By scoring each area from 0 (poor) to 2 (excellent), the framework helps users and developers identify strengths and gaps, ensuring AI supports mental health without compromising safety or human dignity.
3. Communication Strategies for Employee Buy-In
Develop a transparent communication plan. Clearly explain the purpose of the program, how it works, and how employee privacy will be protected. Use town halls, emails, and Q&A sessions to address questions and concerns.
4. Privacy and Ethical Guidelines
Establish clear policies for data privacy, consent, and ethical use of AI. Ensure that employees understand what data is collected, how it will be used, and who will have access to it.
5. Integration with Existing Wellness Programs
Coordinate the new AI solution with your current wellness offerings. Ensure that the AI tool complements, rather than replaces, human support and other resources.
A Journal of Medical Internet Research study pointed out that while chatbots can support mental health care, they should not replace professional diagnosis and treatment.
6. Training Requirements
Provide training for both employees and managers on how to use the AI tool effectively. Offer ongoing support to help everyone feel comfortable and confident with the new technology.
7. Measuring Effectiveness
Set up processes to regularly review the program’s impact. Collect feedback from users, monitor engagement, and evaluate outcomes to identify areas for improvement.
Final Thoughts
Thus, we saw that the workplace mental health crisis demands solutions that are both scalpel-precise and deeply human. As psychologist Dharitri Dutta observes,
AI being easily available and accessible, can help people to easily get connected and seek catharsis, but it fails to provide the true emotional connectedness that a client receives in a therapy session.
The focus should be on creating mental health ecosystems where:
- AI handles the "now": Immediate support, early warnings, and safe spaces for vulnerability.
- Humans nurture the "next": Deep therapeutic work, systemic change, and meaning-making.
Now, you don’t have to choose between physical and mental health; Vantage Fit’s platform fuses both. From guided meditation and mood tracking to expert articles and confidential counselor referrals, it’s a one-stop hub for holistic employee well-being.
Ready to bring true mental health support into your workplace? Schedule your demo today to see how Vantage Fit makes well-being simple, seamless, and truly effective.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can AI work alongside traditional EAP programs?
Absolutely. AI automates check-ins, flags high-risk cases for human counselors, and extends support availability around the clock while easing counselor workloads.
2. Do small businesses need different AI approaches than enterprises?
Yes. Small teams benefit from plug-and-play chatbots and straightforward integrations. Large organizations require scalable platforms with data dashboards, customizable workflows, and multi-language support.
3. Which industries face unique mental health challenges that AI can address?
Manufacturing (burnout detection via wearables), healthcare (predictive analytics for caregiver stress), and high-risk sectors (AI safety monitoring in mining).
4. Can AI chatbots effectively provide mental health support in the workplace?
Partially. Chatbots (e.g., Woebot, Wysa) reduce stigma and offer 24/7 coping strategies, but they lack crisis-handling nuance. Reach out to well-trained professionals for severe issues.
5. How does AI wellness coaching benefit employee mental health?
AI wellness coaching aids in delivering personalized plans (sleep, exercise), detecting burnout via behavioral data, and nudging real-time interventions.
6. What are some of the best AI mental health apps for workplace wellness?
A few of the best AI mental health apps are:
- Wysa: offers 24/7 CBT-based chat support.
- Neurofit: uses somatic exercises and blockchain-secure data for personalized coaching.
- Lyra Health: blends AI with licensed therapists.






